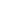
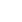The camshaft gear is a crucial component in an engine's valvetrain system, responsible for synchronizing the rotation of the camshaft with the crankshaft. This synchronization ensures that the engine's valves open and close at the correct times, allowing for proper air intake and exhaust flow. Camshaft gears can be made from various materials, including steel, aluminum, or composite polymers, depending on the engine's design and performance requirements.
Over time, camshaft gears can wear out or develop issues, leading to poor engine performance, unusual noises, or even engine failure. In this article, we'll explore two key aspects of camshaft gear maintenance:
Camshaft Gear Noise Symptoms – How to identify if your camshaft gear is failing.
How to Replace Camshaft Gear – A step-by-step guide to replacing a worn or damaged camshaft gear.
1. Camshaft Gear Noise Symptoms
A faulty camshaft gear can produce distinct noises and performance issues. Here are the most common symptoms to watch for:
A. Ticking or Clicking Noises
A worn or misaligned camshaft gear can cause a repetitive ticking or clicking sound, especially at idle or low RPM.
This noise often comes from the timing cover area and may increase with acceleration.
B. Whining or Grinding Sounds
If the gear teeth are damaged or improperly meshed, you may hear a high-pitched whine or grinding noise.
This could indicate excessive wear or lubrication issues.
C. Engine Misfires or Poor Performance
A slipping or misaligned camshaft gear can disrupt valve timing, leading to misfires, rough idling, or power loss.
In severe cases, the engine may not start at all.
D. Check Engine Light
A failing camshaft gear can trigger camshaft position sensor codes (e.g., P0340-P0344) due to improper timing.
If you notice these symptoms, inspect the camshaft gear and timing system immediately to prevent further engine damage.
BMW mini,Peugeot engine timing camshaft sprockets
2. How to Replace Camshaft Gear
Replacing a camshaft gear requires mechanical knowledge and the right tools. Follow these steps for a successful replacement:
Tools & Materials Needed:
New camshaft gear (OEM or performance upgrade)
Timing belt/chain kit (if applicable)
Socket set, torque wrench, and pry tools
Engine locking tools (to maintain timing)
Gasket sealant (if required)
Step-by-Step Replacement Process:
Step 1: Disconnect the Battery & Remove Obstructions
Disconnect the negative battery terminal.
Remove any components blocking access to the timing cover (e.g., serpentine belt, pulleys).
Step 2: Lock the Engine in Position
Use a camshaft locking tool or align timing marks to prevent the engine from moving out of position.
Step 3: Remove the Timing Belt/Chain
Loosen the tensioner and carefully remove the timing belt or chain.
Note: Some engines require camshaft gear removal before accessing the timing components.
Step 4: Remove the Old Camshaft Gear
Unbolt the camshaft gear (some may have a retaining bolt or press-fit design).
Use a gear puller if necessary, but avoid damaging the camshaft.
Step 5: Install the New Camshaft Gear
Align the new gear with the camshaft and secure it with the proper torque specs.
Reinstall the timing belt/chain, ensuring correct alignment with timing marks.
Step 6: Reassemble & Test
Reinstall all removed components and reconnect the battery.
Start the engine and listen for abnormal noises. Verify proper timing with a scan tool if needed.

 English
English Español
Español Deutsch
Deutsch